JS 异步
event loop
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cCOL7MC4Pl0
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eiC58R16hb8
任务队列

渲染

卡顿的本质,而且这也说明事件环可以确保任务在下一次渲染之前完成。

运行逻辑
主要是四个概念组成,调用栈,Web APIs,任务队列,微任务队列。
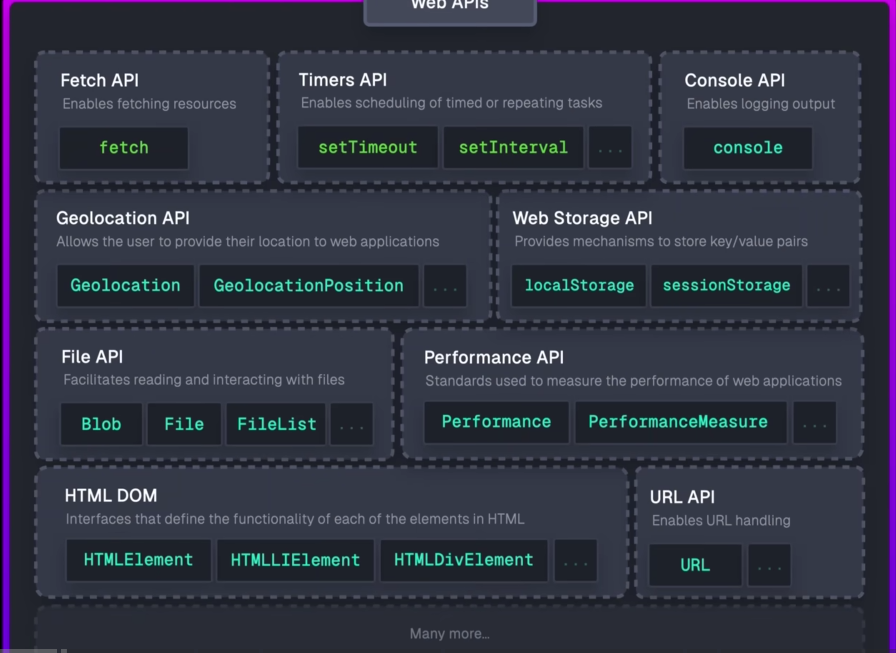
Web API基于 Callbacks 或者 Promise
先调用函数,在 Call Stack 中注册回调,注册完成后就会从 Call Stack 弹出。 这也是为什么我们的界面仍然是可用的。当 API 接收到结果后,不是直接压入 Call Stack,而是将回调压入 Task Queue。(这也是为什么 Task Queue 也被称为 Callback queue)
Task Queue 存储回调和事件处理程序,便于在后续某点执行。
接下来就是 Event Loop 的作用了,它先检查 Call Stack 是否为空,然后从 Task Queue 获取任务并将其移动到 Call Stack。
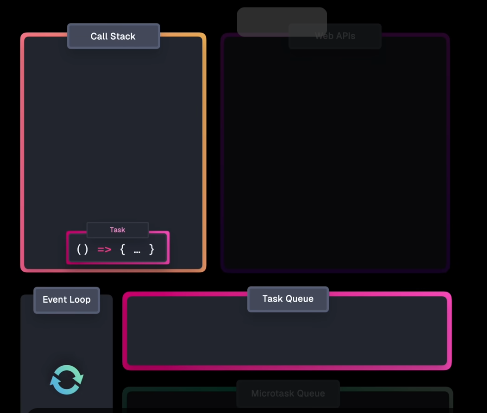
那么,我们也可以对
setTimeout()进一步辨析。它的延时实际上是直到进入Task Queue的时间。
基于 Promise 的回调,使用到的是 Microtask Queue。当 Call Stack 为空时,Event loop 先确保 Microtask Queue 为空,然后才会进入到 Task Queue。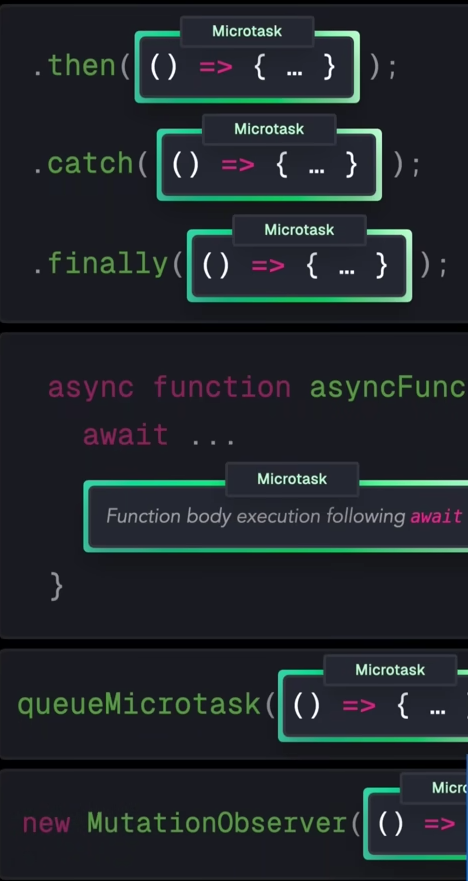
Promise
https://www.joshwcomeau.com/javascript/promises/
从回调函数开始
1 | console.log('1. Before setTimeout'); |
就像我们刚刚讲到的 event loop。先运行执行栈中的全部同步任务,再调用任务队列。
回调地狱
js 的单线程导致了一个问题,js不能用阻塞等待的方式来处理延时或者耗时操作,否则后面的所有任务都会卡住。因而采用异步。
JavaScript 的单线程意味着它的唯一线程既负责执行代码,也负责页面渲染、响应用户交互。
假设 js 线程存在一个阻塞式的
sleep(),那么在这个等待期间, 用户体验会非常糟糕:按钮点击没反应、滚动不了、视频卡住、输入框不能输入。
1 | console.log("3…"); |
从这个角度看,promise 是一种“串联”形式的语法糖
1 | console.log('3'); |
Promise自身
1 | const fetchValue = fetch('/api/get-data'); |
Promise 是 JavaScript 对象。并且存在三种状态
pending,任务还没有完成fulfilled,任务完成rejected,出现了问题。Promise 无法实现
另外,当 Promise 内部任务完成后,它就不再是 pending,而是进入 resolved(已解决)状态。
⚠️ 注意:resolved 不等于 fulfilled(成功)
resolved 的意思只是:有结果了(成功 or 失败)
如果希望在 Promise 被 fulfilled 后注册一些工作来执行。我们可以使用.then()方法来实现这一点。
1 | fetch("/api/data") |
Promise 的使用
对旧 API 的包装
一些旧的 API(比如 setTimeout)是在 Promise 出现之前设计的,它们只支持 回调函数,不支持 Promise。
1 | const demoPromise = new Promise((resolve) => { |
以 setTimeout为例:
1 | function wait(ms) { |
包装好之后,就可以解决掉回调地狱的问题
1 | await wait(1000); |
链式调用
Promise 的一个重要特性是只能 resolved 一次。
Once a Promise has been fulfilled or rejected, it stays that way forever.
1 | window.addEventListener('mousemove', (event) => { |
1 | wait(1000) |
数据传递
1 | function getUser(userId) { |
| 部分 | 解释 |
|---|---|
(user) => { resolve(user); } |
回调函数,数据库查到 user 后调用 resolve,把 user 传给 Promise |
resolve(user) |
把异步结果传递给 Promise,让后续 then 可以接收 |
.then(result => ...) |
result 是回调函数的形参,名字随便,可以用 user、data、x,只要能接收上一步 resolve 的值 |
Rejected
1 | fetch('/api/get-data') |
对于 Promise 的 rejected state,我们使用 catch 来处理。
Async / await
1 | async function addNums(a, b) { |
一旦函数前加上 async:
- 函数自动返回一个 Promise
- 即使函数体是同步运算(像
a + b),返回的也是 Promise
await 的作用:等待 Promise 完成,然后把结果赋值给变量